C# Course – codemeets– 04
Today, we will focus on Control Statements (IF statement, Switch, and Loops) and finally create a Power Calculator for practical learning.
What is a Control Statement?
A control statement determines whether a specific block of code should execute. It helps in decision-making and looping based on conditions.
Types of Control Statements in C#
- IF Statement – Executes code based on a condition.
- Switch Statement – Selects a block of code to execute from multiple options.
- Loops – Repeats a block of code a certain number of times.
IF Statement in C#
An if statement checks a condition, and if it’s true, the code inside runs. The example below demonstrates this concept clearly
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int mark = Convert.ToInt32(85);
if (mark > 50)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pass");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Fail");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
This C sharp code output is given as Pass. Here, if checks if the value of the mark is greater than 50. It is represented as true pass and False as Fail.
else if
This is used to check several conditions at once. look following example will make it clear to you.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int mark = Convert.ToInt32(67);
if (mark > 75)
{
Console.WriteLine("A");
}
else if (mark > 65){
Console.WriteLine("B");
}
else if (mark > 55)
{
Console.WriteLine("C");
}
else if (mark > 40)
{
Console.WriteLine("S");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("F");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
In the example above, the output is B because the condition matched that specific case.
Switch Statement in C#
The switch expression is used to check multiple distinct conditions efficiently. Unlike if statements, switch can check several conditions at once and is often faster when you have multiple potential outcomes.
Here’s how the switch statement works in C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int day = 2;
switch (day)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Sunday");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Monday");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Wrong");
break;
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
This Code output is Monday. A Break statement is use for stop the function.
Loops
Loops have main 3 loops in c#
- For loop
- While loop
- Do While loop
Now I show all loops using Code. See Below all code output is same. output is : 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1.
For loop
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i=10; i >= 1; i--)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
While Loop
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 10;
while (i >= 1)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
i--;
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Do While Loop
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int i = 10;
do
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
i--;
} while (i >= 1);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Now you have very good knowledge about C #. Practice this over and over again. Let us now see how to make a power calculator from what we have learned so far.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("****POWER CALCULATOR****");
Console.WriteLine("Enter Base Number : ");
int x = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter Power Number : ");
int y = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Power is: "+getpow(x,y));
Console.ReadLine();
}
static int getpow(int basenum, int pow)
{
int result = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < pow; i++)
{
result = result * basenum;
}
return result;
}
}
}
Output is Below
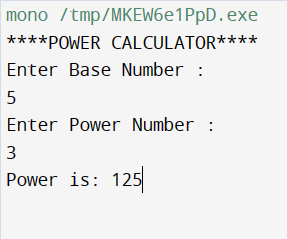
Thank for all!
More C# ClickHere!
See you Next C# Lesson Soon!




thanks, interesting read
very good